Citrus australis v1.0 Assembly & Annotation
Overview
| Analysis Name | Citrus australis v1.0 Assembly & Annotation |
| Sequencing technology | PacBio |
| Assembly method | Hifiasm |
| Release Date | 2023-02-07 |
Nakandala U, Masouleh AK, Smith MW, Furtado A, Mason P, Constantin L, Henry RJ. Haplotype resolved chromosome level genome assembly of Citrus australis reveals disease resistance and other citrus specific genes. Hortic Res. 2023 Apr 3;10(5):uhad058. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhad058.
AbstractRecent advances in genome sequencing and assembly techniques have made it possible to achieve chromosome level reference genomes for citrus. Relatively few genomes have been anchored at the chromosome level and/or are haplotype phased, with the available genomes of varying accuracy and completeness. We now report a phased high-quality chromosome level genome assembly for an Australian native citrus species; Citrus australis (round lime) using highly accurate PacBio HiFi long reads, complemented with Hi-C scaffolding. Hifiasm with Hi-C integrated assembly resulted in a 331 Mb genome of C. australis with two haplotypes of nine pseudochromosomes with an N50 of 36.3 Mb and 98.8% genome assembly completeness (BUSCO). Repeat analysis showed that more than 50% of the genome contained interspersed repeats. Among them, LTR elements were the predominant type (21.0%), of which LTR Gypsy (9.8%) and LTR copia (7.7%) elements were the most abundant repeats. A total of 29 464 genes and 32 009 transcripts were identified in the genome. Of these, 28 222 CDS (25 753 genes) had BLAST hits and 21 401 CDS (75.8%) were annotated with at least one GO term. Citrus specific genes for antimicrobial peptides, defense, volatile compounds and acidity regulation were identified. The synteny analysis showed conserved regions between the two haplotypes with some structural variations in Chromosomes 2, 4, 7 and 8. This chromosome scale, and haplotype resolved C. australis genome will facilitate the study of important genes for citrus breeding and will also allow the enhanced definition of the evolutionary relationships between wild and domesticated citrus species.
Assembly statistics
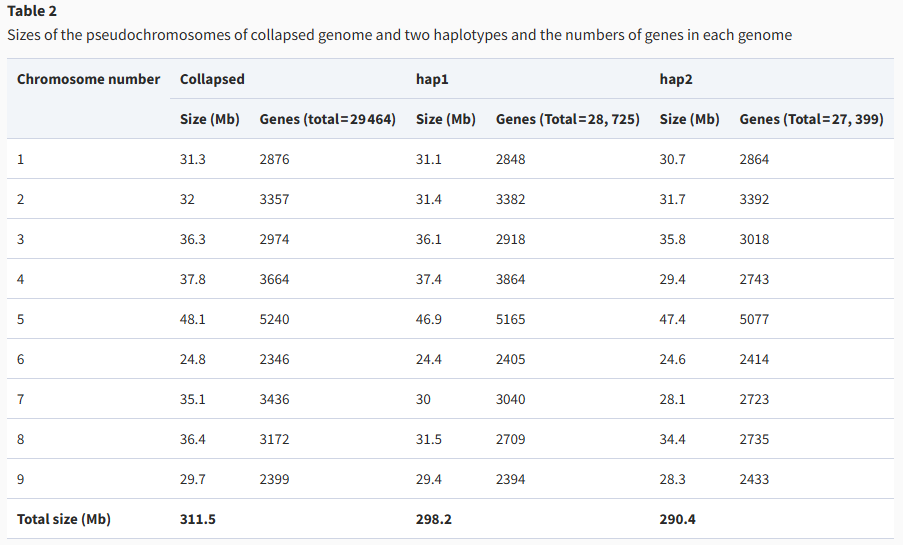
Assembly
The Citrus australis v1.0 Assembly file is available in FASTA format.
Downloads
| Chromosomes (FASTA file) | GWHBQDX00000000.genome.fasta.gz |
Gene Predictions
The Citrus australis v1.0 genome gene prediction files are available in GFF3 and FASTA format.
Downloads
| Genes (GFF3 file) | GWHBQDX00000000.gff.gz |
| CDS sequences (FASTA file) | GWHBQDX00000000.CDS.fasta.gz |
| Protein sequences (FASTA file) | GWHBQDX00000000.Protein.faa.gz |
Functional Analysis
Functional annotation for the Citrus australis v1.0 is available for download below. The proteins were analyzed using InterProScan to assign InterPro domains(Pfam).
Downloads
| Domain from InterProScan | Citrus_australis_v1.0.Pfam.tsv.gz |
S genes
Summary
| Query | Chr | Size(bp) | Coordinates | BLASTn Hit | BLASTn %ID | Domain |
| SLF1 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30087325-30088425 | ASM2964120v1, SLF1-2 | 97.548 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF2 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30105588-30106712 | PP719841.1, S30-SLF2 | 92.192 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF3 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30116756-30117877 | PP719842.1, S30-SLF3 | 92.87 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF4 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30135591-30136658 | PP719843.1, S30-SLF4 | 91.927 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF8 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30223846-30222707 | PP719833.1, S2-SLF8 | 87.642 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF9 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30266971-30265829 | ASM2964120v1, SLF9 | 91.419 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF7 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30285781-30286911 | PP719832.1, S2-SLF7 | 93.369 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF6 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30294550-30295692 | PP719845.1, S30-SLF6 | 90.901 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF5 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30301116-30299989 | PP719830.1, S2-SLF5 | 89.6 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF10 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30326439-30327584 | PP719835.1, S2-SLF10 | 94.318 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF11 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30340821-30339646 | ASM2964120v1, SLF11 | 98.639 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF12 | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30344970-30343849 | PP719837.1, S2-SLF12 | 99.109 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF13ψ | Chr1 | 31296472 | 30355546-30356621 | PP719853.1, S30-SLF13 | 98.329 | - |
Citrus S genes Nucleotide
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF1 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF2 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF3 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF4 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF8 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF9 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF7 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF6 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF5 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF10 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF11 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF12 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF13ψ mRNA, complete cds
Citrus S genes Protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF1 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF2 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF3 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF4 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF8 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF9 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF7 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF6 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF5 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF10 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF11 protein
- Citrus australis v1.0 SLF12 protein